WHY UV?
UV Disinfection Research & Studies
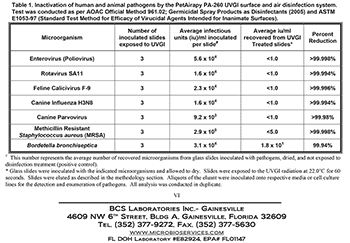
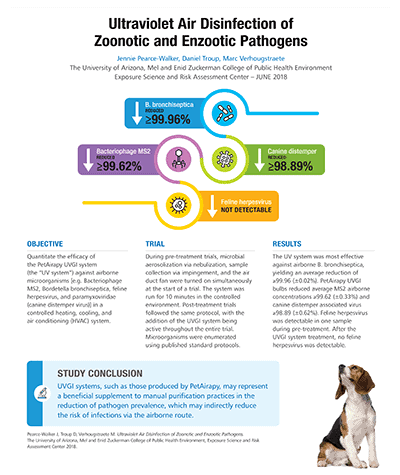
We take pride in backing our UV disinfection technology with research, studies, and tests.
Since our founding, we have strived to ensure we can deliver the results you need for your animal care environment. As part of our ongoing mission, we work with researchers and scientists in university and field studies, as well as independent test laboratories. The following highlights our tests and studies to date, which include air and surface disinfection and real-world field studies.